#todo god help me
Definition
An object is considered symmetrical if it does not change after a set of transformations. These transformations can include:
- Reflection - Flipping an object around a line (for 2D objects) or plane (for 3D Objects).
Translation
- Translations - Moving the object in a certain direction. Most finite objects are translationally asymmetrical. Infinite objects, however, are usually translationally symmetric. To visualise this, imagine you have a viewport through which you can see objects. If the viewport changes during a translation, the object inside the viewport is translationally asymmetric.
Rotational
Rotating the object around a point or line. Various 2D objects have different degrees (or order) of rotational symmetry, which symbolise how many orientations the object can be in and look the same.
Scaling
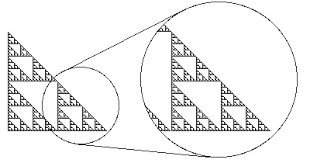
- Scaling. Very few objects possess scale symmetry, but notable exceptions are fractals (when scaled to certain amounts):