A stack is a linear, abstract, data structure in which items are accessed in a Last In First Out (LIFO) order. Specifically, it means items inserted first into the stack are removed last, and vice versa. It can be likened to a stack of plates, where a plate at the bottom can only be removed until the ones above it are. Stacks are heavily used in ‘depth-first’ style algorithms, such as depth first search, pre-order tree traversal and more.
Definition
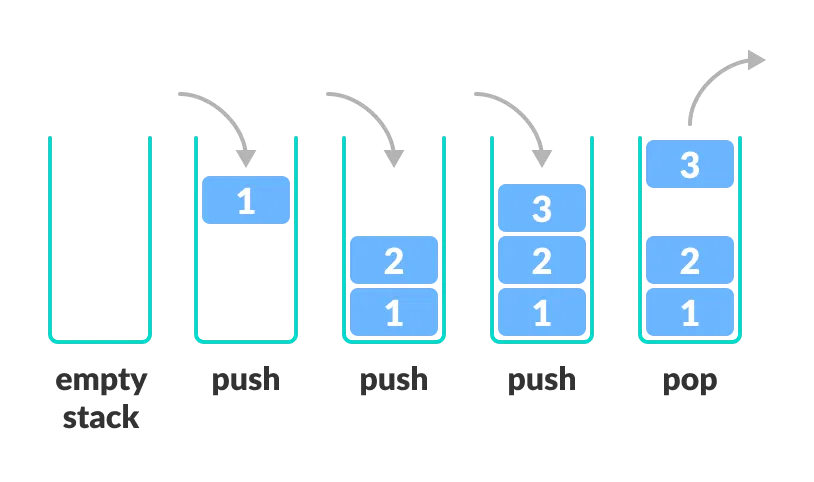
- Items are accessed in Last In First Out (LIFO) order
- Only the top (head) can be viewed (via peek) or returned (via pop)
- Adding new items is referred to as pushing
- Removing items is referred to as popping
- The last item to enter a stack is the first to come out of it
ADT Signature
name stack;
import elem, boolean;
ops:
newStack : → stack;
push : stack × elem → stack;
pop : stack → stack;
top : stack → elem;
isEmpty : stack → boolean;
etc.
Time Complexity Analysis
Unsorted Array
We can use an unsorted array to store a stack, where pushing is putting elements at the end of the array, and popping is removing from the end. Peek is just looking up the last index of the array.
Basic Operation: Array Access
Assumptions:
- = The underlying array used to store the stack
- = The number of elements in the stack
| Operation | Worst Case (WC) | Best Case (BC) | Average Case (AC) | Case descriptions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Push | Equivalent to insertion of an element after index . Array insertion after end takes constant time | |||
| Pop | Equivalent to deleting the last element. Takes constant time. | |||
| Peek | Assuming we keep track of , this is equivalent to array access, as we simply return which is constant time. |
Singly Linked List
We can implement a stack using a linked list as well. We push elements by inserting them to the tail of the list, and pop elements by deleting from the tail. Alternatively, we can also push and pop by inserting and deleting from the head, since the time complexity is equivalent.
Basic Operation: Traversing to the next node of a linked list.
Assumptions:
- = Linked list
- = Head of the list
- = Tail of the list
| Operation | Worst Case (WC) | Best Case (BC) | Average Case (AC) | Case descriptions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Push | Equivalent to insertion at tail/head of a linked list, which always takes constant time | |||
| Pop | Equivalent to deletion from the tail/head of a linked list, which is also constant time. | |||
| Peek | Getting the tail/head is always constant time. |