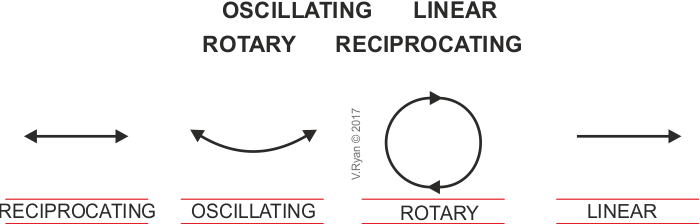
Motion refers to the way an object moves over a period of time. In VCE Systems Engineering, there are 4 main types of motion:
- Linear: Movement in a straight line. Common examples include a car moving along the road, a screw going into a board, etc.
- Rotary: Rotational movement i.e. spinning. Wheels spinning, a screw spinning as it goes inside a board, gears, etc. are all examples of rotary motion
- Reciprocating: A type of linear motion, where an object repeats the same pattern over a period i.e. back-and-forth movement. The most common example is a piston, but even sawing a board is considered reciprocating, as the saw moves back-and-forth
- Oscillating: A type of rotary motion around a pivot, i.e. arcing movement. For example, a pendulum arcs around a pivot, so it is an example of oscillating movement. Another example would be swings.

A system can have many types of motion, not just a single, obvious one
Conversion of Motion
Many machines, simple and complex, are used to convert motion from one form into another:
- Rack & Pinion Gears convert rotary motion into linear motion
- Crankshafts convert, reciprocating motion (of the pistons) into rotary motion
- Slider-crank linages convert rotary motion into reciprocating motion, or vice versa.
#todo more examples